Surface
Surface
Water-repellent (antifouling) / hydrophilic / photocatalytic surfaces
Controlling the surface free energy of solids enables to change surface properties.
Water-repellent (antifouling) surfaces
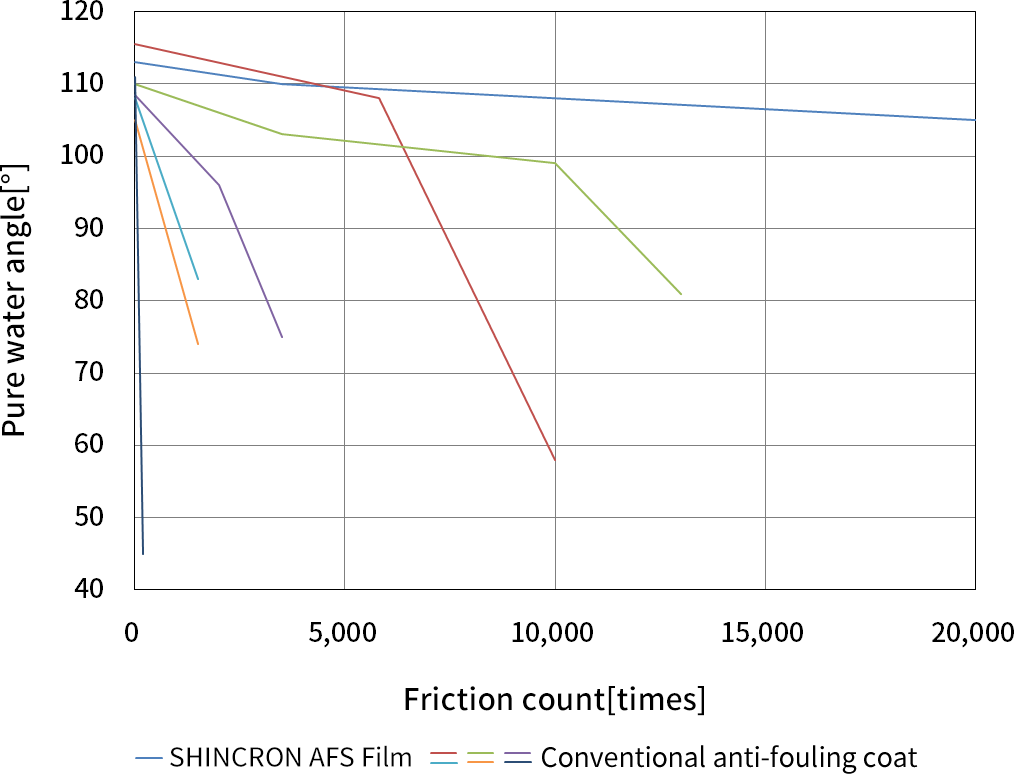
Water-repellent films with high durability can be formed.
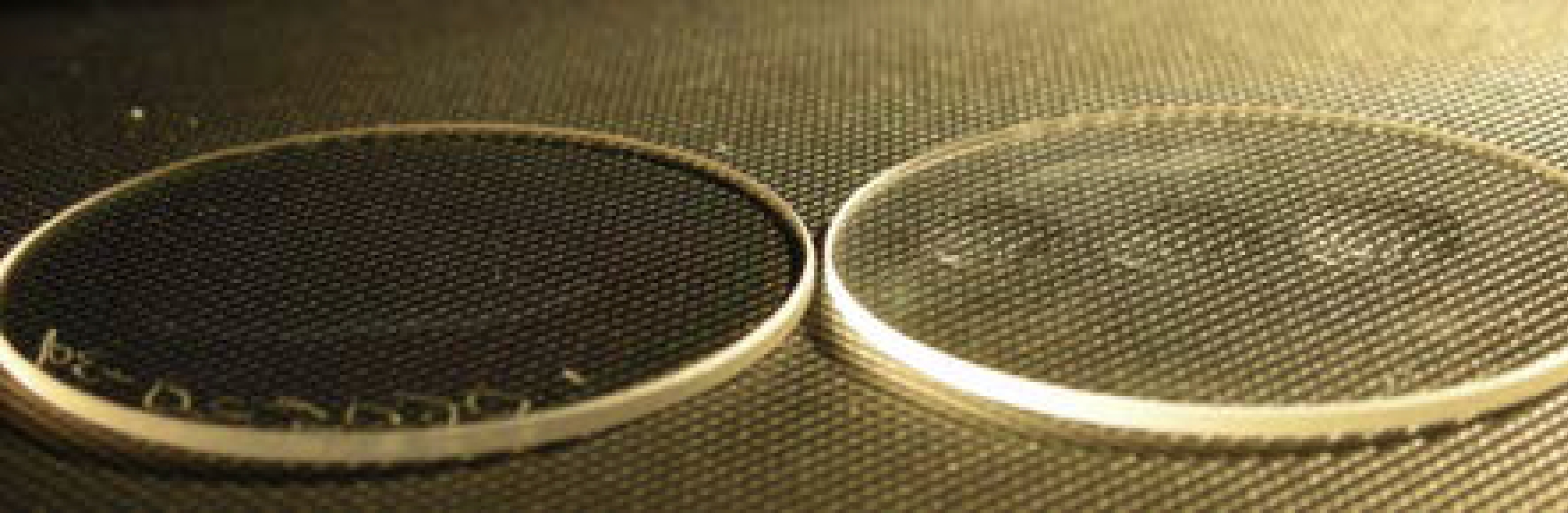
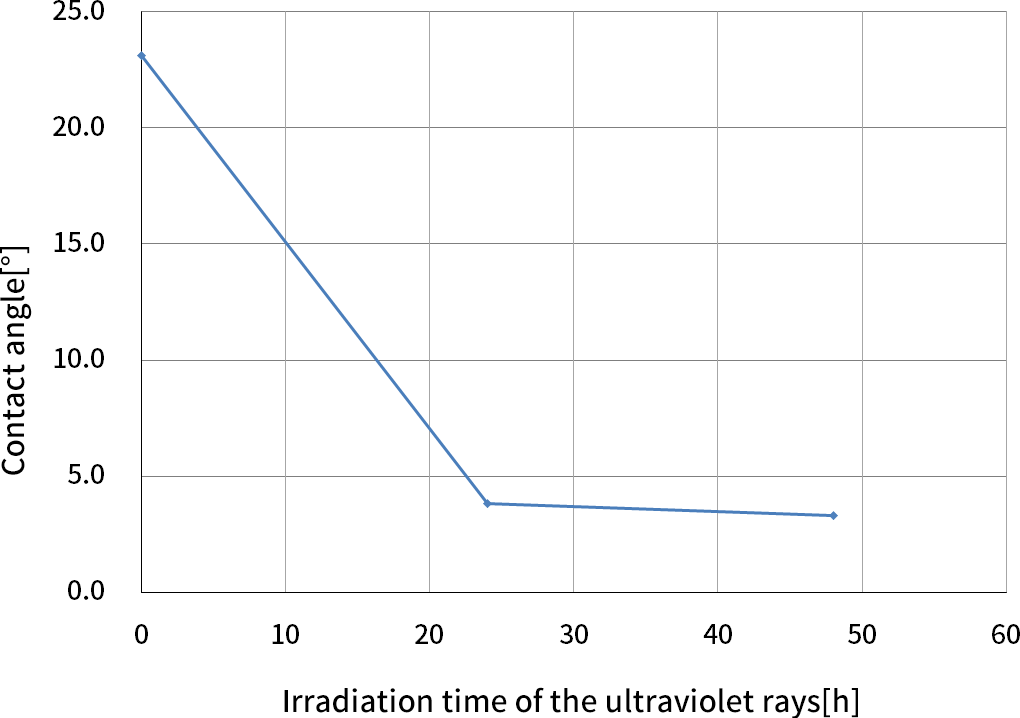
Hydrophilic surfaces
| Contact angle | |
|---|---|
| Glass (without AFS coating) | 20° |
| Glass (with AFS coating) | 5° |

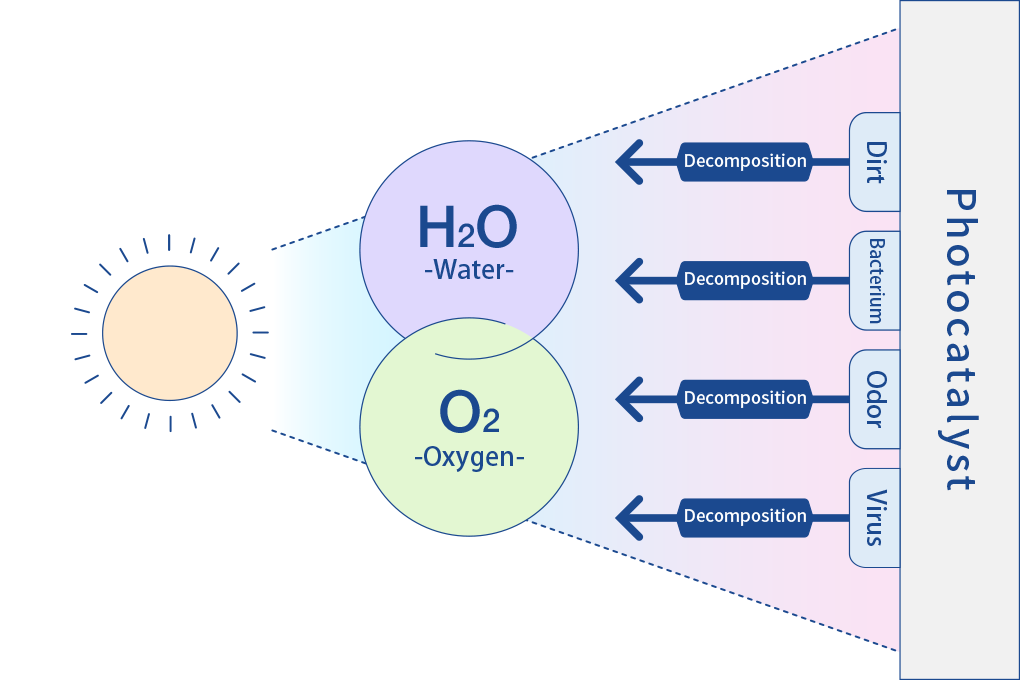
Photocatalytic surfaces
Surfaces coated with titanium oxide, which is a standard material for photocatalysts, become highly hydrophilic, and water forms a thin film to flow on such surfaces. In addition, oxygen contained in titanium oxide is extracted by light irradiation and reacts with water molecules to form hydroxyl groups to make the surfaces hydrophilic. In this way, dirt is washed away and the self-cleaning effect is retained for a long time.
Rigid films
DLC, SiN, SiC, and SiAlON films can be formed as a high-hardness surface treatment that can bear chemical corrosion and friction.
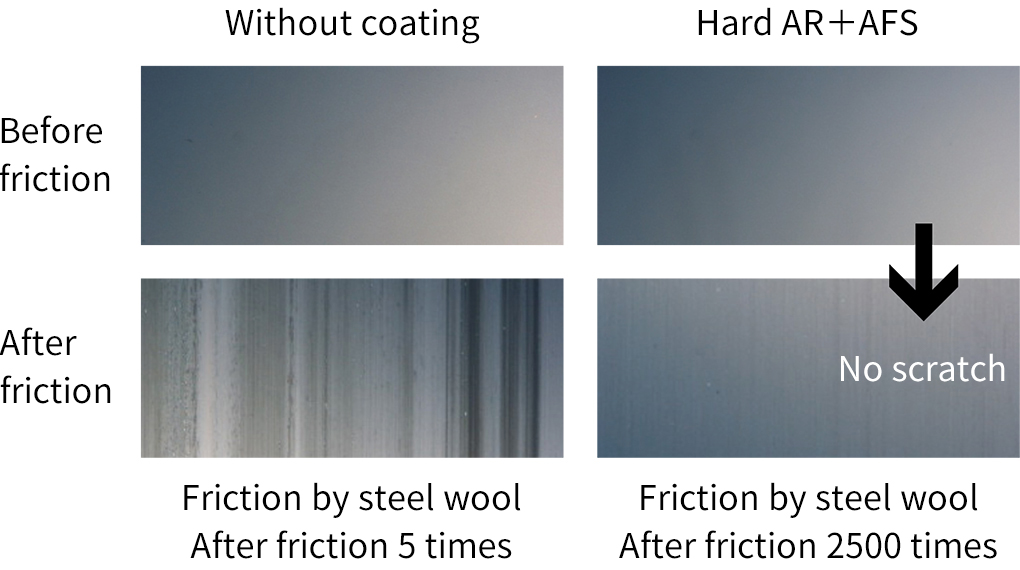
Microscope photographs of a hard AR + AFS film after a friction test with steel wool (x 50)
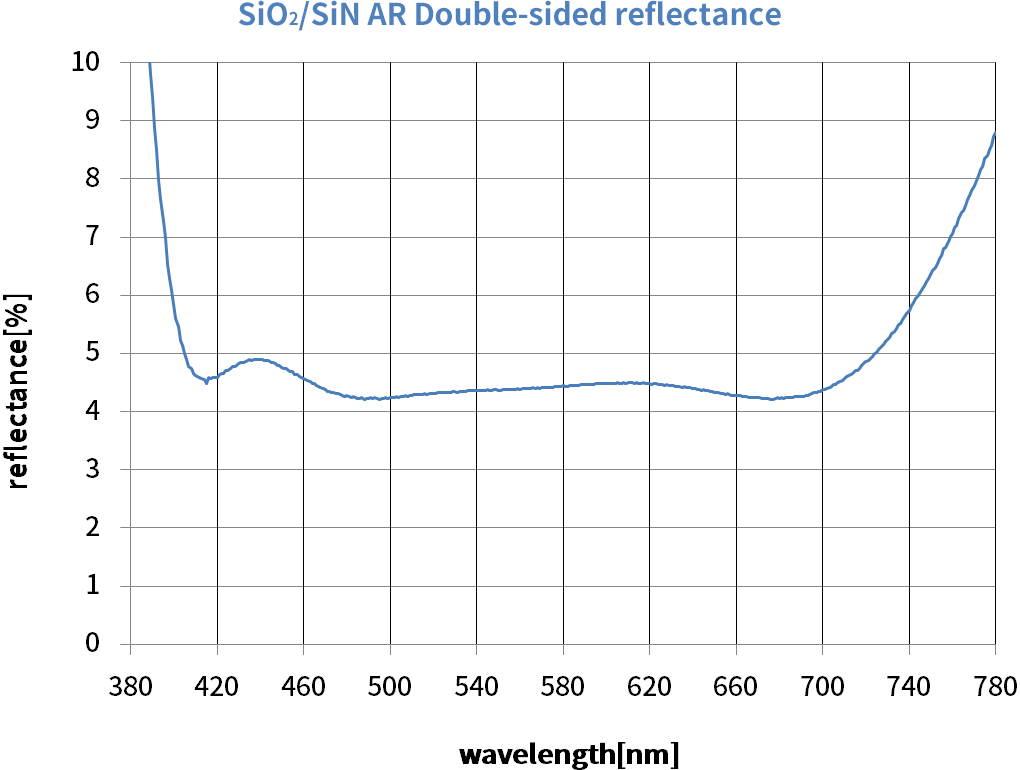
AR film using Si3N4, which is a transparent hard material, as a highly refractive material.
Compared to AR films made with glass or other materials, this film has higher rigidity and scratch-resistance.
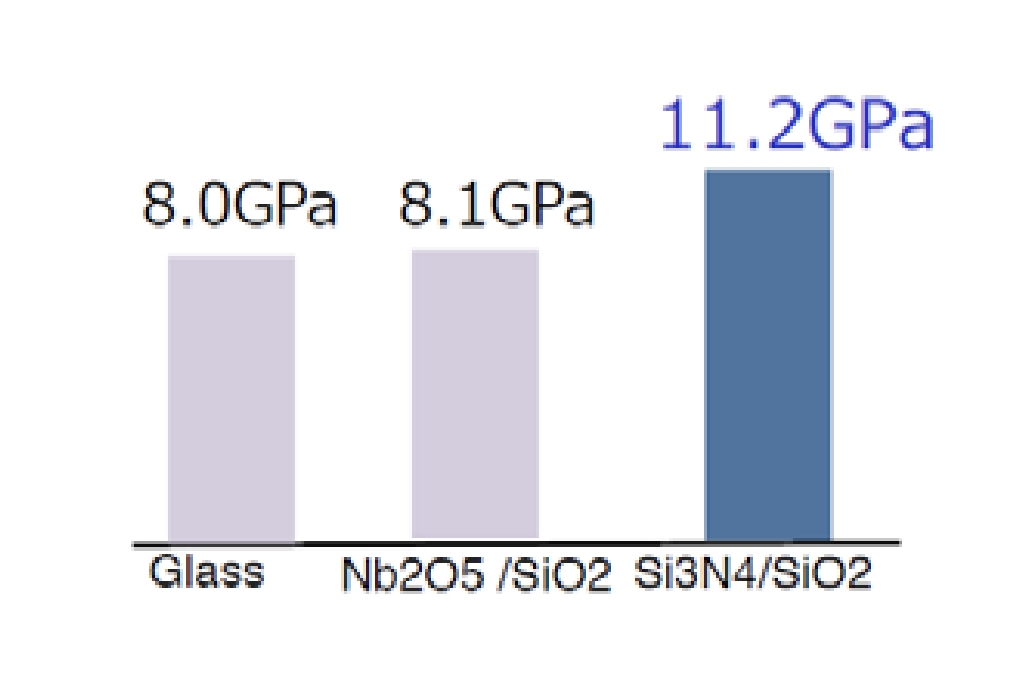
Nanoindenter hardness of the AR film

A microscopic image taken after a test conducted using a cutter knife under a load of 1 kg